Published: 2026-01-01
Journal: Genome Biology and Evolution
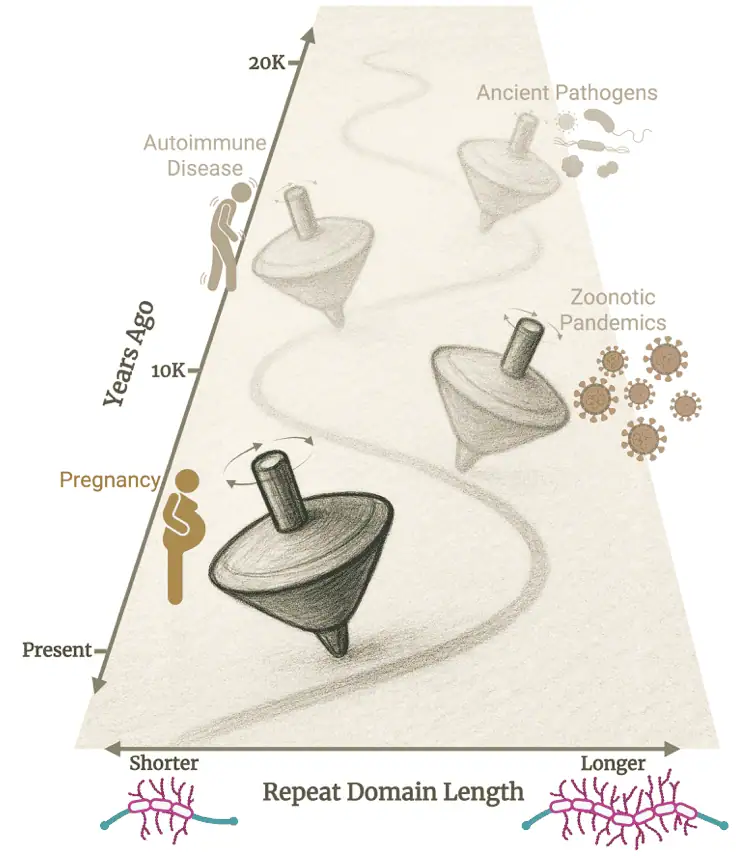
Abstract Understanding genomic function has historically relied on sequence conservation across evolutionary time. However, advances in genomics have revealed that functional
Published: 2025-03-24
Journal: Nucleic Acids Research, Volume 53
Abstract Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus-like particles (VLPs) are ∼100-nm-sized bioinspired mimetics of the authentic virus. We undertook
Published: 2024-10-24
Journal: Science
Structured Abstract INTRODUCTION Human adaptation to a wide range of diets is a hallmark of our species, sometimes even reflected in our
Published: 2025-08-22
Journal: Genome Biology and Evolution
Abstract Genes within the secretory calcium-binding phosphoprotein (SCPP) family evolved in conjunction with major evolutionary milestones: the formation of a calcified
Published: 2023-11-28
Journal: bioRxiv
Abstract: Starch digestion is a cornerstone of human nutrition. The amylase enzyme, which digests starch, plays a key role in starch
Published: 2023-07-03
Journal: Communications Biology
Abstract Chemosensation (olfaction, taste) is essential for detecting and assessing foods, such that dietary shifts elicit evolutionary changes in vertebrate chemosensory
Published: 2022-08-26
Journal: SCIENCE ADVANCES
Abstract How novel gene functions evolve is a fundamental question in biology. Mucin proteins, a functionally but not evolutionarily defined group
Published: 2020-04-16
Journal: Journal of Virology
ABSTRACT Sialic acids (Sia) are the primary receptors for influenza viruses and are widely displayed on cell surfaces and in secreted
Published: 2019-05-14
Journal: eLife
Abstract The amylase gene (AMY), which codes for a starch-digesting enzyme in animals, underwent several gene copy number gains in humans
Published: 2016-12-05
Journal: BMC Ecology and Evolution
Abstract Background A common, 32kb deletion of LCE3B and LCE3C genes is strongly associated with psoriasis. We recently found that this deletion is ancient, predating Human-Denisovan